
Speech-language pathologists provide services and support for families and their children to address delays and disabilities in communication, language, speech, emergent literacy and feeding/swallowing. Effective communication is fundamental to all aspects of human functioning, particularly learning and social interaction.
You may want to discuss with your child’s doctor the need to seek an evaluation with a licensed Speech-language Pathologist if your child exhibits any of the following:
- Is having difficulty with feeding or swallowing
- Shows poor ability to follow simple directions and /or limited ability to receptively identify items/objects by 18 months
- Says only a few sounds, words or gestures by 18-24 months
- Does not combine words at 2 years
- Shows any regression in speech or language development
- Has poor social interaction/inappropriate use of language- limited eye caze, does not respond to name, repetitive behaviors or speech (i.e. lining cars/toys up over and over or repeating words, sounds or phrases over and over
- Has speech that is extremely difficult to understand past the age of 24 months
- Struggles to say sounds or words (30-36 months)

What Is A Language Disorder?
Some children have problems with understanding, also called receptive language. They may have trouble:
- Understanding what gestures mean
- Following directions
- Answering questions
- Identifying objects and pictures
- Taking turns when talking with others
Some children have problems talking, also called expressive language. They may have trouble:
- Asking questions
- Naming objects
- Using gestures
- Putting words together into sentences
- Learning songs and rhymes
- Using correct pronouns, like “he” or “they”
- Knowing how to start a conversation and keep it going
Many children have problems with both understanding and talking. Some children also have trouble with early reading and writing, such as:
- Holding a book right side up
- Looking at pictures in a book and turning pages
- Telling a story with a beginning, a middle, and an end
- Naming letters and numbers
- Learning the alphabet

What Is A Speech Disorder?
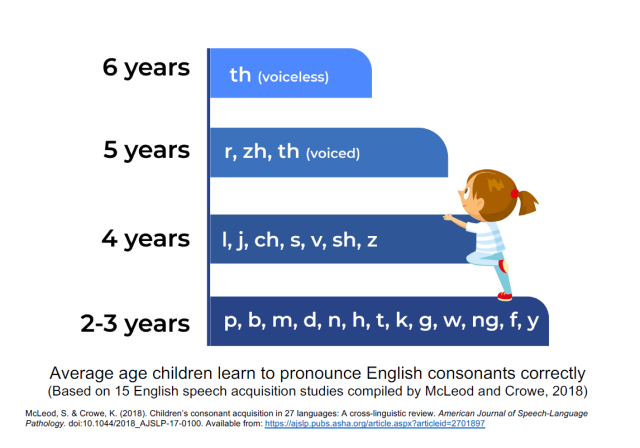
Most children make some mistakes as they learn to say new words. A speech sound disorder occurs when mistakes continue past a certain age. Every sound has a different range of ages when the child should make the sound correctly. Speech sound disorders include problems with articulation (making sounds) and phonological processes(sound patterns).
To see the age range during which most children develop each sound, see the chart referencing developmental milestones for speech sound acquisition below.
Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) is a motor speech disorder. Children with CAS have problems saying sounds, syllables, and words. This is not because of muscle weakness or paralysis. The is caused when the brain has problems planning to move the body parts (e.g., lips, jaw, tongue) needed for speech. The child knows what he or she wants to say, but his/her brain has difficulty coordinating the muscle movements necessary to say those words. Skilled, intensive speech therapy can help children with CAS and articulation/phonological disorders improve their ability to speak more clearly.

What Is A Voice Disorder?
Voice disorders are classified as problems with voice quality, loudness, pitch, and resonance. The major cause of voice disorders in children is vocal abuse (using the vocal cords incorrectly and in a damaging way).
The speech-language pathologist can assist the child by identifying situations that promote poor vocal habits along with teaching proper vocal hygiene.

What Is A Fluency Disorder?
Stuttering is a disorder of speech that affects the fluent production of sounds, words, phrases, and sentences. Types of disfluencies include part-word repetitions (“d-d-d-dog”), prolongations (“b___oy”), broken words (“lis-ten”), whole word repetitions (“She She She”), phrase repetitions (“I want to, I want to go”), and interjections (“um”).
In addition, secondary behaviors may occur. These behaviors are particular to the individual and develop as the individual tries to cope with his stuttering. Occasionally children experience a period of disfluency between the ages of three and six.
These are normal disfluencies and can be characterized by interjections, whole word repetitions, and phrase repetitions.

What Is Augmentative And Alternative Communication?
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) includes all forms of communication (other than oral speech) that are used to express thoughts, needs, wants, and ideas. We all use AAC when we make facial expressions or gestures, use symbols or pictures, or write. People with severe speech or language problems rely on AAC to supplement existing speech or replace speech that is not functional.
Special augmentative aids, such as picture and symbol communication boards and electronic devices, are available to help people express themselves. This may increase social interaction, school performance, and feelings of self-worth.
Schedule An Evaluation
If you have concerns regarding your child’s communication skills, contact Chatterbox Pediatric Therapy to schedule an evaluation.